Setting up Vectorstore with Qdrant
A vector database is a specialized database created to transform data, typically textual data, into multi-dimensional vectors, also referred to as vector embeddings, and store them systematically. These vectors serve as mathematical representations of attributes or features. The dimensionality of each vector can vary significantly, ranging from a few dimensions to several thousand, depending on the complexity and granularity of the data.
In this book, we’re going to cover the 4 open-source vector databases: Qdrant, FAISS, Supabase and Chroma. They’re standard and straight-forward. An important consideration is the necessity of consistently utilizing the same embedding model for both embedding the data into VectorStore and conducting similarity searches within VectorStore at a later stage.
We will begin with Qdrant, our choice for several reasons:
- It is open-source.
- It is straightforward and lightweight.
- It operates independently without dependencies, capable of standalone execution.
- It includes a user-friendly GUI for convenient collection and point management.
Start Qdrant with Docker:
The following code shows how to start Qdrant with mounting its persistent storage. In this instance, the source on the host, the working directory is in /$DIR/qdrant_storage and the target mount point in the container /qdrant/storage. The :z option tells Docker that the volume content will be shared between containers
sudo systemctl restart docker
docker run -p 6333:6333 -p 6334:6334 \
-v /$DIR/qdrant_storage:/qdrant/storage:z \
-td qdrant/qdrantAfter Qdrant is launched completely, you can browse https://localhost:6333/dashboard and view the following or similar.
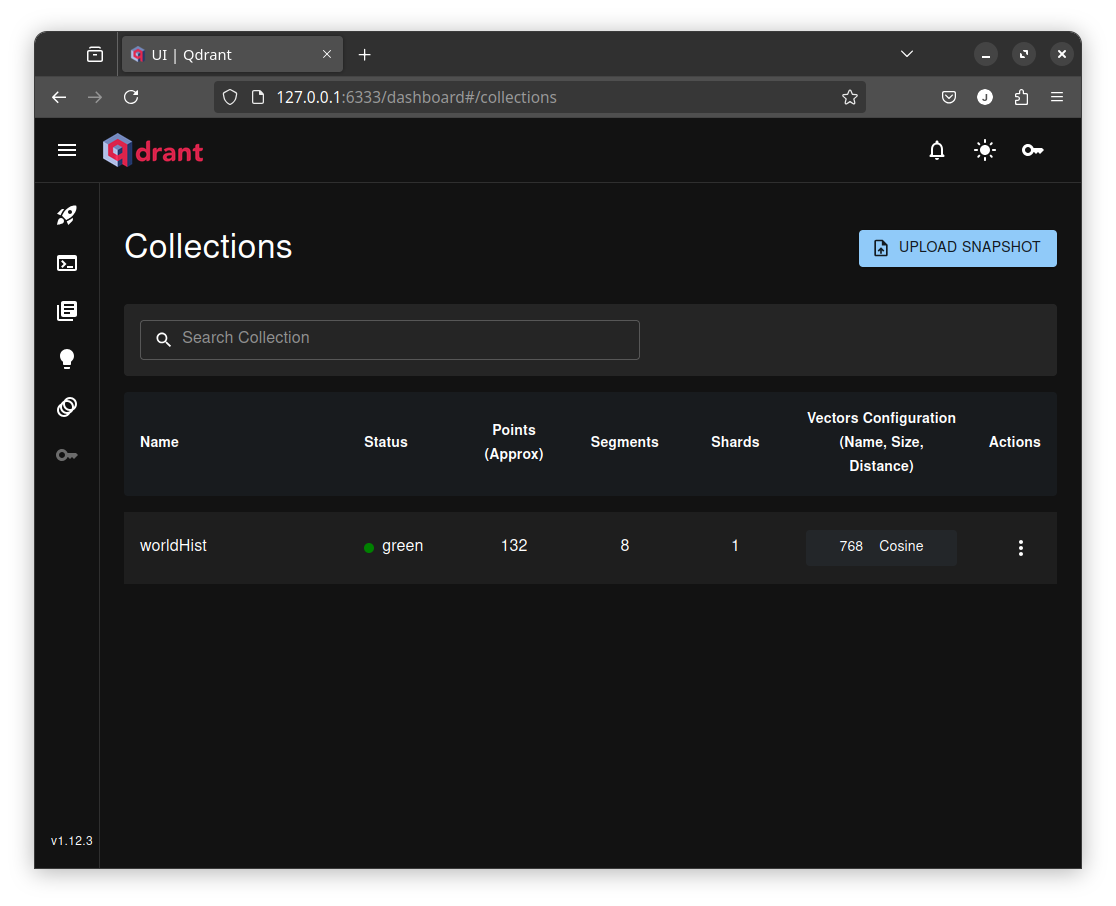
 Figure 4.2 Qdrant Dashboard Sample
Figure 4.2 Qdrant Dashboard Sample
Please be aware that this service is accessible to anyone within the same network. This means that anyone who can access the URL has the ability to view and potentially delete your data. Therefore, it is essential to implement HTTP Basic Authentication to restrict access. For example, if using Nginx, refer to the documentation > https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/security-controls/configuring-http-basic-authentication/
Qdrant is a powerful and flexible vector database. You can find more detailed information at https://qdrant.tech/documentation/quick-start/
At this moment, the Qdrant vector database is ready for use.