Document Summarization
In the previous chapters, we discussed the key components and features of LangChain, along with instructions on setting up a development environment. Our next step involves integrating these elements into a practical case study.
Business Scenario
Let’s say that there are numerous interconnected documents, sharing similar narratives within a specific domain such as sales strategies or human resource policies. The goal is to develop a bot capable of comprehending these documents and responding to user queries based on the information contained within. All data, queries, responses, and computational processes will be confined within an internal network to ensure data security compliance within the enterprise. Additionally, the outcomes of user queries and the bot’s responses can be stored for potential future analytics purposes.
Technical Objective
To kick off the project, let’s delve into the code step by step. Typically, there are four key stages involved:
- Loading the document file and segmenting it into chunks.
- Embedding the chunks into a vector database.
- Conducting a similarity search.
- Optimizing the results semantically.
In this technical endeavor:
- All components in this setup are open-source.
- Qdrant will be utilized within a Docker environment to maintain persistent VectorStore functionality.
- Mistral LLM serves as the Language Model (LLM).
- Ollama acts as the platform for LLM operations.
- LangChain integrates a standard Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) approach to execute the chain.
Hardware Specification
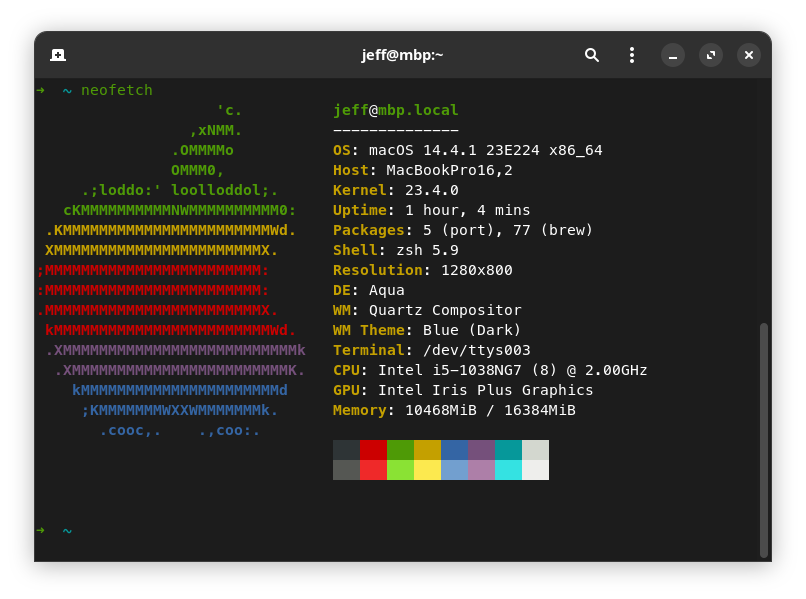
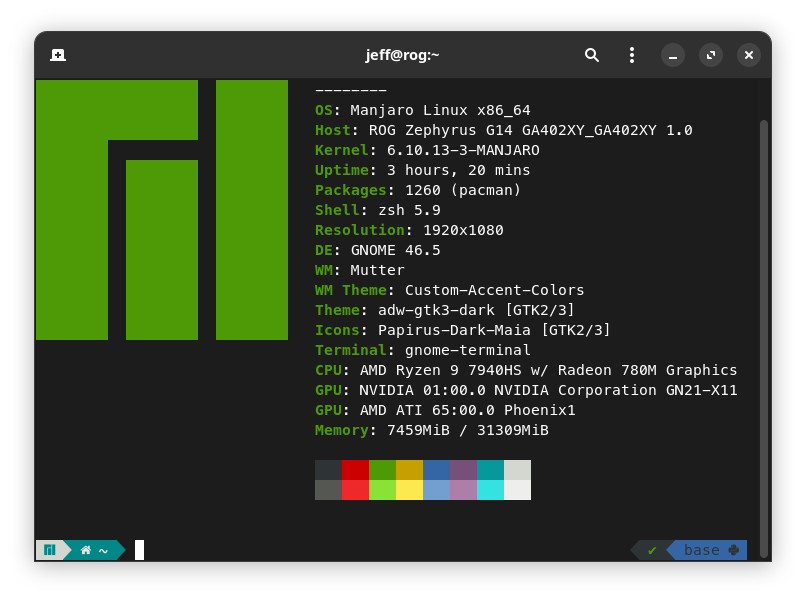
I have 2 laptops at home for leisure and work. One is MacBook Pro 16,2 (16G RAM, Intel i5 CPU, no GPU) and another ROG G14 (32G RAM with CPU and 16G RAM with Nvidia GPU)
The code example provided in this book can run on both macOS Sonoma 14.4 and Manjaro Linux with kernel 6.10.13.